What are the Benefits and Challenges of Peer-to-Peer Payment Apps?
17 Jul 23 


Fintech app development is expanding rapidly, so companies want to take advantage of the shifting fintech trends. Since digital payments continue to be the most well-liked fintech company area, there is rising demand for creating payment applications. The banking industry’s technological developments are setting cash aside with the increasing digital transformation.
The digital transformation in the banking industry is bringing novel and innovative financial products. One such financial product is the Peer-to-peer payment app. Peer-to-peer payments’ increasing acceptance recently has only strengthened this tendency. According to calculations, the total value of transactions made using payment apps in 2022 will be $8,563 billion.
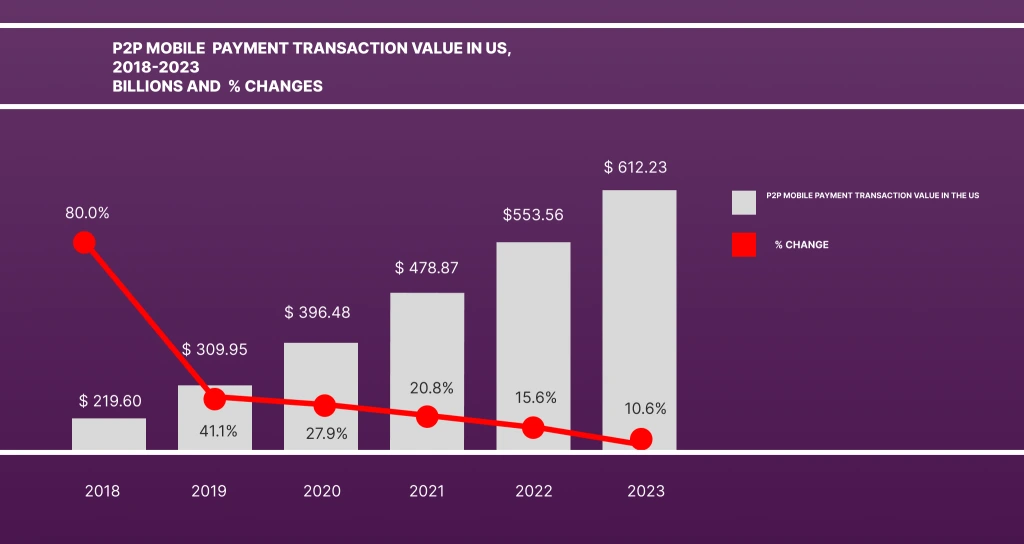
P2P mobile payment customers make up 148.8 million US smartphone consumers, or over 62%, based on eMarketer. As the peer-to-peer payments market expands, over 180 billion individuals will engage in P2P transactions in 2026. EMarketer predicts that P2P payments will surpass the $550 billion milestone in 2022. It will grow by 10.5% in 2023, to roughly $612 billion.
These numbers show that the P2P payments business is continually growing. So there’s a good possibility of being prosperous if your goals call for creating a peer-to-peer payment app. However, making a P2P payment app is difficult because of several technological, privacy, and legal challenges. Here, we will discuss the difficulties and opportunities of P2P payment applications.
What are Peer-to-Peer Payment Apps?
A peer-to-peer (P2P) payment app is an online service that enables individuals to transfer funds to “peers,” who can be friends, family members, or in some circumstances, businesses. Peer-to-peer (P2P) apps offer the ease of instantaneous money transfers among both parties without the need for mediators.
The Covid-19 epidemic has positively responded to the concept of cashless banking or contactless payment methods. People choose a safer alternative that requires no actual money. They can pair and fill an e-wallet with funds from their financial institution or credit card via payment applications, enabling contactless transfers to friends or merchants.
Navigate the lists below to understand why P2P payment apps have become popular.
- A sizable unexplored market for virtual banking goods remains since 31% of individuals lacked a bank account as of 2017.
- In 2020, Apple Pay held a market share of over 90% for mobile wallets in the US.
- Based on a poll conducted in 2021, 29% of Americans opted to use a mobile payment app to make purchases.
- In 2021, 42 percent of US individuals sent cash to people they knew.
- In the US, a digital wallet is the most popular payment method, making up 30% of transactions.
- In 2026, an estimated 5,197.75 million people will utilize digital payment applications for transactions.
Major Features of P2P Payment Apps
- Signing up
The P2P payment services require users to sign up using phone numbers or social networking accounts, similar to a mobile wallet platform. Customers can add their bank credentials and debit or credit card information after their initial login has been validated. However, standalone payment apps like PayPal don’t demand that you instantly provide bank details.
- Transfer & Receive Funds
Customers have the choice of sending any amount in their digital wallets that is accessible to the chosen recipient. They may get funds from people who have sent them.
- Send Bill/Invoice
It enables users to send bills or invoices to those paying for particular goods or services. The peer-to-peer payment software must also create and transmit the invoice to senders and receivers.
- History of Transactions
This option displays an overview of every payment on a weekly, monthly, and annual schedule. This function is offered to users of all digital payment solutions. The users of this service can view the transaction history at their convenience, which increases flexibility.
- Push Messages
Push alerts can provide information on various subjects, including ticket reservations, deadlines, rewards points, etc. The peer-to-peer payment application’s biggest feature is this. Each payment-related action is broadcast to consumers via push messages.
- Multi-Factor Authentication
Misuse by unauthorized persons is guarded against the payment app using multi-factor authentication, OTP, PIN, and biometric validation. These safety tokens also prevent clients from unintentionally starting payments.
- Transfer
Consumers may send cash to payment gateways, financial institutions, and companies in their home country or other currencies.
- Integrated Finance
The program becomes simpler to use by adding support for sending money to bank institutions in addition to peer-to-peer transfers.
- Biometric Authentication
A fingerprint lock is a great supplementary security measure to stop anyone from opening the payment app. The safety of consumers is safeguarded, and it avoids the unintentional disclosure of private financial information.
- Sending Texts
P2P payment apps benefit from having a collaborative message feature to communicate with other users. It controls discourse and focuses it on topics related to business dealings.
- E-Wallet
P2P software might become a comprehensive digital payment solution incorporating digital wallets. Customers rarely misplace their cash or ATM cards due to this function, which takes the role of virtual wallets.
It can be done by logging into the digital wallet via different mobile phones or gadgets, regardless of whether an individual misplaces the mobile phone. A user’s specific login and password can always secure the amount.
- Customer Service
When users encounter technological, transactional, or other issues with the app, an AI-based chatbot and information base assist in directing them to solutions.
P2P Payment: How Does It Work?
As previously indicated, P2P (peer-to-peer) payment programs allow one account holder to digitally send money to several accounts without using cash or a chequebook. In this part, we’ll examine how P2P payments via apps function in real life and the typical procedures users take to complete the transaction. Here are some important actions:
- Complete the Signup Process, then log in
It’s straightforward to establish a peer-to-peer payment account. Regardless of the platform you select, you must first register on the app by providing private data like your name, bank contact information, address, city, etc. After that, you need to input a PIN or a strong password.
- Select payee
This particular one is among the most crucial elements in the peer-to-peer payment procedure. You must satisfy the KYC procedure after finishing the registration process. The information of the individual you wish to pay is then added. The user will want the recipient’s name to complete this step.
- Set the amount
The sender must next specify how much money they wish to send. The user may optionally specify the rationale for the payment in addition to this. This item, however, may be optional.
- Input password to validate the payment
The customer must type in the password they created when they signed up, or they can authorize the money transaction using an OTP. An individual can set up a safety query if he forgets his password.
- Receiving money
After that, a payment receipt you can download or print is instantly created. Keep a record of your financial activities in this way.
Types of P2P Payment Apps
When creating a peer-to-peer payment app, a thorough study is required, much as when creating an iOS or Android app. These four peer-to-peer payment app categories are typical.

- Mobile OS-Based Apps
Apple Pay and Android Pay are the corresponding names of Apple and Google’s payment applications. These applications or features only permit money transactions within their environments. In developed nations with extensive payment infrastructure, this technique is quite effective. Customers who are adept at technology accept this concept. This architecture relies on tokenization and fingerprint verification for secure and quick transactions.
- Banks-Oriented Apps
Dwolla and ClearXchange are a few instances. Many financial institutions have specialized mobile payment software or hardware built to function with a particular Point-of-Sale (POS). Direct withdrawals from or deposits into bank accounts are possible with these apps. In this case, the mobile network operator must guarantee QoS (Quality of Service).
- Standalone Apps
PayPal and Square Case are two examples. P2P payments are available through these online and offline applications, using bank accounts or accounts with saved cash. By default, these applications contain eWallet functionality, enabling users to easily store or transfer money to others. It is appropriate to note that no banks have supported or backed these applications. Users in undeveloped nations can employ this non-bank model’s advantages.
- Social Media or Messaging Based Apps
SnapChat and Square Cash are two examples. Transferring periodic payments to our connections via social networks is helpful. Since many transactions are made between frequent references, these applications do not need strict verification before starting the process. These applications can reduce processing resistance throughout the board. In India, WhatsApp is testing a text-based payment service.
P2P payment programs have been quite prevalent recently across the globe. They have a greater adoption rate than bank payment applications in many areas. Peer-to-peer transactions made via mobile phones are anticipated to hit $612.23 billion in the US alone by 2023, according to a study by eMarketer. Due to their exceptional performance and intuitive design, peer-to-peer payment services are becoming increasingly prevalent. Let’s move into the development process of a P2P Payment App.
Development Process of a P2P Payment App
It would be best to search for an opportunity to develop a peer-to-peer payment app. To design a peer-to-peer payment application that produces the greatest results, you must keep the following processes in mind:
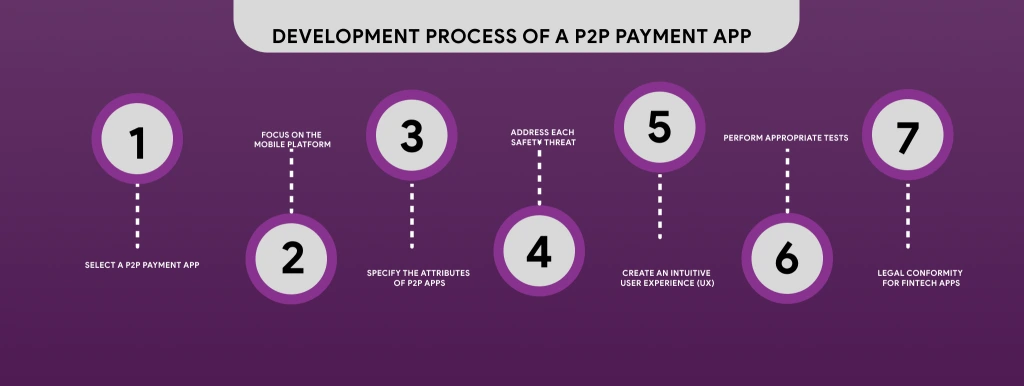
- Select a P2P Payment App
You must initially select the nature of your P2P app among standalone services and financial institutions. You may also choose to create applications that enable instant transactions in addition to that. As a result, consider your options and decide decisively.
- Focus on the Mobile Platform
You may select either iOS or Android as your device of choice if your app’s cost is low or constrained. This can assist your business in a couple of ways. Initially, it will reduce the cost of developing your P2P applications, and secondly, it will provide you with greater insight into your consumer base.
- Specify the Attributes of P2P Apps
In your software, create an MVP (minimum viable product). You may include more important functions in your app.
- Address each Safety Threat
Make safety precautions a part of mobile devices, and maintain them. Usage must be made of face recognition apps, fingerprint scanners, and additional safe payment tools. Two-factor authentication must be enabled at minimum, though, if the user’s gadget cannot handle it.
The best solution for the payment privacy problem is a two-factor authorization. A second security component is needed in addition to the password required for permission, such as an SMS containing a code to verify.
- Create an Intuitive User Experience (UX)
Your P2P payments app’s user interface and user experience must be clear and easy. How things operate must be obvious because your customers are not interested in trying to figure it out. So don’t make the app’s UI/UX design more intricate.
- Perform Appropriate Tests
The efficacy of a P2P app depends on testing. QA engineers do each sort of testing to assist you in finding and fixing issues as soon as possible. You may even locate a group of individuals evaluating your app’s payment gateway in beta.
- Legal Conformity for Fintech Apps
If you’re developing a FinTech app, adhere to PCI-DSS, or Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard. Because of this, you must ensure that your P2P payment application meets all PCI-DSS rules. Additionally, get a PCI-DSS certificate to promote openness and confidence.
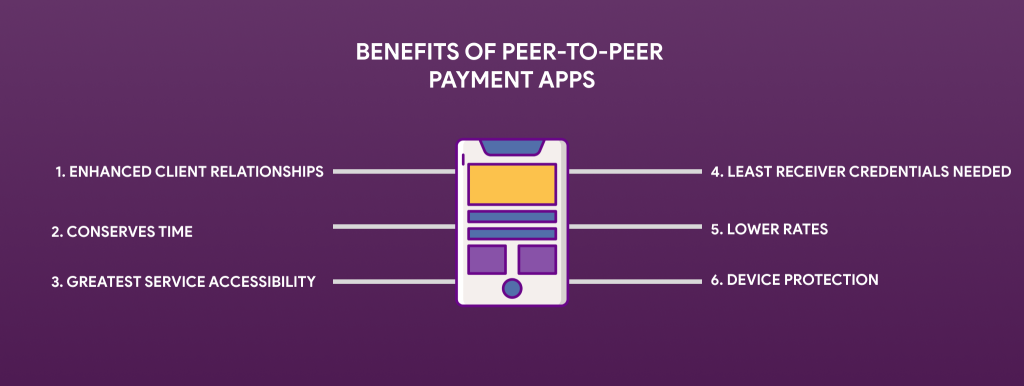
Benefits of Peer-to-Peer Payment Apps

1. Enhanced Client Relationships
One advantage of creating a P2P payment app is the chance to enhance client interactions. As we’ve recently indicated, providing customers with an extra payment option would greatly improve the image of many companies.
2. Conserves Time
Do you recall when transferring currency to someone else took a lot of time? You had to go to a bank location individually, wait in line, and do other comparable and tedious tasks. Sophisticated digital payment solutions simplified things but didn’t improve the issue because we still needed to provide lots of information and fill out several sections. Fortunately, peer-to-peer mobile payment apps have emerged as a great solution.
The following benefits help them reduce time:
- The effortless application implies that there are simply a couple of easy stages in the complete payment procedure.
- An intuitive interface for interacting and communicating with others.
- Rapid transactional times
- An array of service options
3. Greatest Service Accessibility
Anyone, at any time and anywhere, may use peer-to-peer payment solutions since they:
- You only need an internet connection; no territorial connection is required.
- Don’t count on the timing aspect because transactional solutions are accessible every day of the year.
- Various systems may reinforce it, so you can use any gadget to do business.
4. Least Receiver Credentials Needed
As we’ve previously mentioned, one advantage of a P2P money transfer app is that it needs to know just a minimal amount of information about the money transfer receiver. This, among other benefits, makes the payment process simpler and quicker.
5. Lower Rates
P2P payments are popular with consumers because they often have cheaper fees than traditional payment mediators impose. Therefore, by creating a money transfer app, you assist your consumers in making a little investment.
6. Device Protection
Every P2P payment is regarded as trustworthy and secure. Privacy is guaranteed once the cardholder is linked to the 3-D encrypted structure. A global PCI DSS certificate is also required to provide 3-D encrypted solutions.
Challenges for Peer-to-Peer Payment Apps
Creating a P2P payment app is far more difficult than creating apps for businesses. A rapid fix for these issues is necessary since they will influence the app’s final launch.
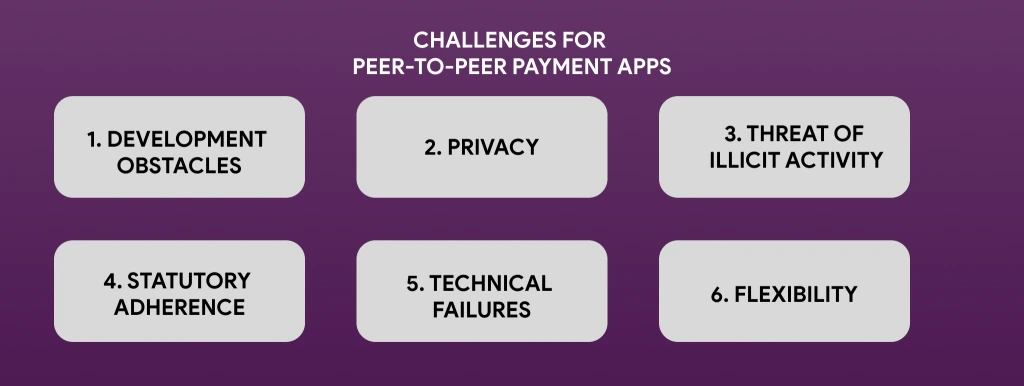
1. Development Obstacles
A rapidly expanding audience and greater visibility come after an effective launch. Without flexibility in consideration, your payment app may encounter obstacles that will cause service interruptions, unpredictability, and a rapid turnover rate. Utilize flexible cloud services, technology elements, and microservices to prepare your app for future expansion. Create an independent monetary computation component to reduce the basic payment system’s undue strain.
2. Privacy
Customers trust P2P payment companies always to preserve their confidentiality. It can be damaging if attackers access personal details, past transactions, or confidential banking data. Service suppliers must take precautions, such as explicitly guaranteeing cloud security and posting their confidentiality agreements.
3. Threat of Illicit Activity
Customers may have a billion dollars in their e-wallets, making payment applications important for financial interfaces. Ensuring the app is secure is essential since unauthorized entry might lead to illicit activity. Designers must ensure that financial information is transported across devices, computers, or gadgets using encryption and adding security measures like two-step authentication.
4. Statutory Adherence
Every feature added to the application must be compatible with legal organizations to function lawfully. For example, payment applications that gather credit card information follow the PCI DSS. Payment applications must strictly follow Know-Your-Customer (KYC) laws like FinCEN’s CDD rule to avoid illicit financing.
5. Technical Failures
Experts collaboratively develop a P2P payment app from various software fields. It demands a team of exceptionally competent professionals and is not a task that can be handed off to a freelancer. Several interconnected components, such as a digital wallet, blockchain technology, encoding, APIs, and other cutting-edge technology, make up a payment app.
6. Flexibility
The criteria for the fintech business of mobile payments are constantly shifting. Supporting simple payment methods is key, but it’s just as important to comprehend user behavior and adjust the app as necessary. For instance, P2P-only software would need to interface with taxi services, or it could become irrelevant.
Wrapping Up
Peer-to-peer payment apps are becoming more popular with both consumers and banks. This software may elevate your company by creating an innovative source of income as a strong and dependable payment service. The world is quickly moving towards using online payment methods. Thus, now is the perfect opportunity to create a unique P2P application.
Mindster is a top-notch mobile app development company providing fintech app development services. By integrating cutting-edge technology and consumer expectations, we specialize in creating mobile app solutions for our users. Our talented and experienced UI/UX design team develops stunning, user-friendly financial apps for peer-to-peer payment.
Do you have any thoughts about creating mobile applications? Please consult with our specialist right away!
- Android Development3
- Artificial Intelligence17
- Classified App1
- Digital Transformation7
- Doctor Appointment Booking App10
- Dropshipping1
- Ecommerce Apps27
- Education Apps2
- Fintech-Apps30
- Flutter2
- Flutter Apps19
- Food Delivery App5
- Grocery App Development1
- Grocery Apps3
- Health Care4
- IoT2
- Loyalty Programs8
- Microsoft1
- Mobile App Maintenance1
- Mobile Apps116
- Product Engineering2
- Progressive Web Apps1
- Saas Application2
- Shopify3
- Software Development1
- Taxi Booking Apps7
- Truck Booking App5
- UI UX Design8
- Uncategorized2



















Comments