How can Near-Field Communication (NFC) be Used in Healthcare?
14 Feb 25 


Healthcare is growing rapidly among numerous businesses utilizing Near Field Communication (NFC) to enhance comfort, boost productivity, and streamline procedures. Thus, NFC in healthcare has a huge significance. According to a recent analysis from Transparency Market Research (TMR), healthcare sector is one of NFC’s rapidly expanding markets. This statistics is with a CAGR of 20.4%. The healthcare sector undergoes a significant transformation.
This is because many individuals use digital transformation tools to track their health and participate more actively in healthcare choices. The increasing use of mobile health and innovative medical devices provides novel possibilities for device makers. This is in line with changing consumer expectations.
Problem Statement
Device manufacturers must provide a customized experience to differentiate themselves from their rivals. This is because the demand for networked medical devices becomes increasingly saturated. Therefore, why concentrate so much? Several factors. The most crucial aspect of NFC in healthcare is it offers the high level of privacy for safeguarding medical data. NFC is simple to operate, easily accessible, and affordable to install.
What is NFC?
Near-field communication (NFC) is when two devices are in contact or placed near just a few centimeters, a short-range wireless networking technology utilizes magnetic field induction to permit interaction between them. This covers credit card authentication, granting physical accessibility, transmitting small files, and launching more robust wireless networks. In general, it expands and develops upon the work of current ecosystems and norms surrounding radio frequency ID tags (RFID)
NFC adds dynamic elements to RFID and contactless technology that is possible by contemporary cell phones. All modern phones accept NFC chips and services like Apple Pay and Google Pay with billions of RFID tags and terminals currently in use, .
Numerous cards loads into one mobile device more easily using NFC for payments, public transport, establishing accessibility, unlocking auto doors, and other scenarios. NFC enables mobile apps based on fundamental RFID features, such as automated Bluetooth headphone pairing and Wi-Fi connectivity. A billboard or advertisement may also immediately pull up data or an app.
How Does NFC Work?
NFC is built on three essential technological advancements to allow different applications (nfc healthcare). This includes wireless tag readers, credit card processing using cryptography, and P2P, or peer-to-peer, communication. NFC is built by the establishment of the RFID series of norms and requirements, including ISO/IEC 14443 and ISO/IEC 15963 (nfc in healthcare). These use a wireless connection method that operates on principles distinct from those used by typical wireless radios.
NFC sends messages via magnetic field induction (as utilized in mobile healthcare system using nfc technology), unlike most radios, which use radio wave transmission. NFC data is transmitted at a frequency of 13.56 MHz, or a wavelength of 22 meters. The fact that the field passes away much faster than radio waves makes using induction coupling to convey data more advantageous than using radio waves.
This helps eliminate eavesdropping on private conversations concerning the usage of credit cards, unlocking codes, and other personal data (nfc for pervasive healthcare monitoring). The second significant NFC breakthrough is the application of encrypted contactless credit card processing (nfc based secure mobile healthcare system).
Due to public-key cryptography, the card may produce a unique verification code for every transaction without disclosing the card’s internal data or the three-digit bank code. It also guarantees that the original card information is not obtained, regardless of whether individuals tuned in or a hacker checked a card on a crowded tube.
The foundation by the NFC Forum, a not-for-profit industry group, uses these two components as to add P2P connections to the ISO/IEC 18092 standard. Traditional RFID and credit card use cases require a single direction, active card reader to read a passive tag or card.
Numerous competent devices, such as mobile devices, headsets, routers, household items, and manufacturing machinery, may now start or respond to NFC inquiries because of standards developed by the NFC forum. This allowed for a wide variety of relationships and communication patterns.
The sharing of information is simpler, while reducing security flaws required an extensive amount of work. For instance, you can use Android Beam to tap two cell phones simultaneously to exchange contact information, but you can’t unintentionally transfer executable programs, which could transmit a virus.
Suppliers of smartphones are beginning to add some basic application running features above this. A smart tag within the Google ecosystem may open a browser-based dynamic web app.
Apple just released Apple App Clips, which enable users to start apps with minimal functionality for things like buying food or activating a scooter rental kiosk without downloading a full-fledged app. These applications aren’t allowed to obtain private information on the mobile device.
Benefits of NFC
NFC offers a number of practical advantages, such as the following:
- The ability to pick among a variety of cards rapidly
- Greater privacy than standard credit cards
- Enhanced productivity for payment processors
- More straightforward to use for customers to pay for items
- Easier to obtain back-end data
- Enabling quick establishment of novel links
How NFC is Used in Healthcare?
Few industries hold the promise of NFC as brightly as the medical sector. The simplicity, privacy, and predictability provided by NFC favours in healthcare over the difficulties of healthcare organizations. This is based on the enormous variety of medical operations, emergency treatment requirements, and the different healthcare activities performed in hospitals at any one time.
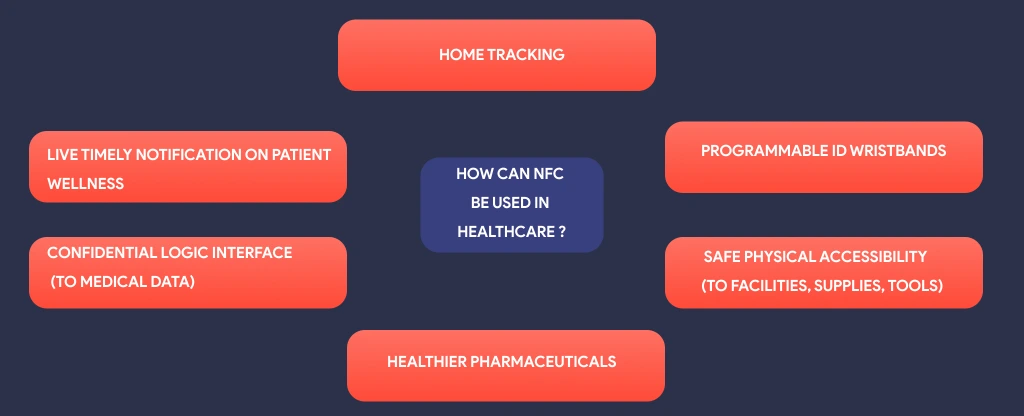
Live Timely Notification on Patient Wellness
The patient’s location, the time since the nurse visited, and the current therapy a doctor gives are all known by medical personnel in real-time. You can collect data, keep in access-controlled databases, and give access in a variety of forms to streamline documentation, logistics, and prevent mistakes.
NFC tags and wristbands with NFC capabilities replaces the conventional wristbands that gets attached by patients. These device refreshes periodically with data. This includes when a drug is previously administered or which treatment has to be done.
Confidential Logic interface (To medical data)
When sensitive medical data is present, a digital environment requires the same level of security as a real one. Healthcare professionals need easy access to databases and information to deliver the best treatment possible. It is simple and safe to safeguard information and facilitate everyday chores like upgrading files and reviewing records using NFC to limit access to PCs, tablets, and other devices.
Home Tracking
NFC in healthcare offers new home monitoring opportunities as an NFC-enabled bracelet is set-up to check vital signs. A medical expert can see the patient’s medical data in the doctor’s office once The patient touches the bracelet while using a tablet or smartphone. Others who are recuperating from an illness or surgery can go home sooner, while others with chronic problems can see a caregiver less frequently.
Programmable ID Wristbands
NFC in healthcare is helpful in normal circumstances as well. NFC-enabled wristbands may substitute metallic “Medic-Alert” wristbands for those with severe health conditions, including asthma, diabetes, or allergies to foods or drugs, and provide medical personnel with more information.
Safe Physical Accessibility (To facilities, supplies, tools)
Some places are accessible to anyone, and regions that don’t exist at many healthcare organizations, like hospitals, treatment centres, medical facilities, and supermarkets. Only authorized employees should have permission to use items like pharmacy cabinets or operating rooms. Thus, you must keep these locations segregated.
Healthier Pharmaceuticals
You can check the drug’s validity when NFC tag attaches to a medication’s box or labeling, . Also you can examine dose information, or learn about adverse reactions and associated drugs. This is possible by simply pressing the tag using your smartphone or tablet. The tag may also offer connections to websites, data, repeat requests, or phone numbers for healthcare providers.
We anticipate NFC in healthcare taking on a significant role in improving healthcare by lowering costs, boosting productivity, and optimizing results in healthcare settings and at residence as the sector proceeds to implement the innovation.
Final Thoughts
The use of NFC technology in healthcare applications is expanding quickly. Because of its excellent application and adaptability, NFC can be a helpful technology in hospital and home healthcare environments. Because software is simple to deploy, low commitment means designing novel medical options, and the possibilities among designers are expanding.
- Android Development3
- Artificial Intelligence27
- Classified App3
- Custom App Development2
- Digital Transformation11
- Doctor Appointment Booking App13
- Dropshipping1
- Ecommerce Apps38
- Education Apps2
- Fintech-Apps35
- Fitness App2
- Flutter3
- Flutter Apps19
- Food Delivery App5
- Grocery App Development1
- Grocery Apps3
- Health Care7
- IoT2
- Loyalty Programs9
- Matrimony Apps1
- Microsoft1
- Mobile App Maintenance2
- Mobile Apps120
- Product Engineering5
- Progressive Web Apps1
- Saas Application2
- Shopify7
- Software Development1
- Taxi Booking Apps7
- Truck Booking App5
- UI UX Design8
- Uncategorized4
- Web App Development1



















Comments