The shift to Small Language Models (SLMs) isn’t just a technical trend—it is the ultimate move for companies prioritizing sovereignty, speed, and 90% cost efficiency.
In the early days of the generative AI boom, the “bigger is better” philosophy reigned supreme. Every enterprise scrambled to integrate trillion-parameter models, assuming that sheer size was a prerequisite for business intelligence.
However, as we move into 2026, the honeymoon phase of “General-Purpose AI” is ending. Companies are waking up to a brutal reality: what costs $50,000 for a pilot project often balloons into $5 million in production. The solution? Small Language Models (SLMs).
What exactly is an SLM?
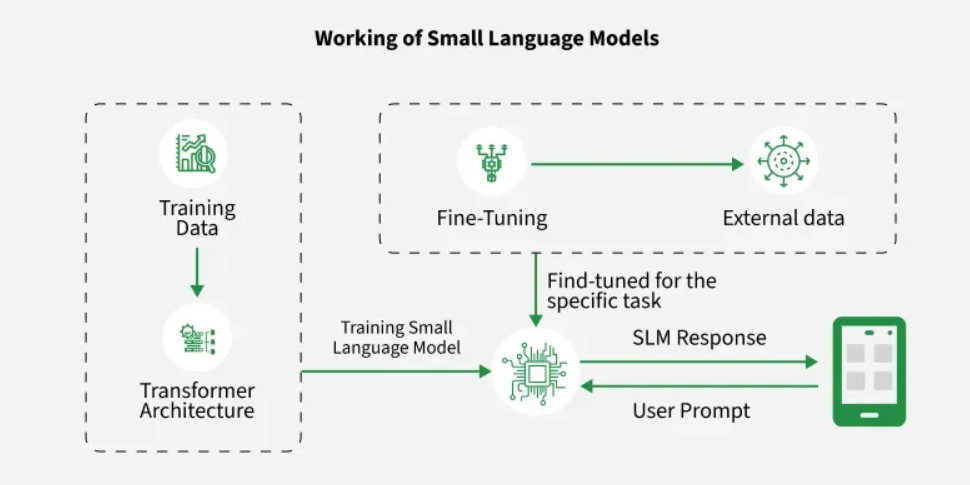
Technically, an SLM is a generative AI model typically defined by having fewer than 10 billion parameters (some as small as 100 million). Unlike Large Language Models (LLMs) that try to know everything about everything, SLMs are trained on extremely high-quality, “textbook-grade” datasets. This allows them to mimic the reasoning of giants like GPT-5 within specific domains.
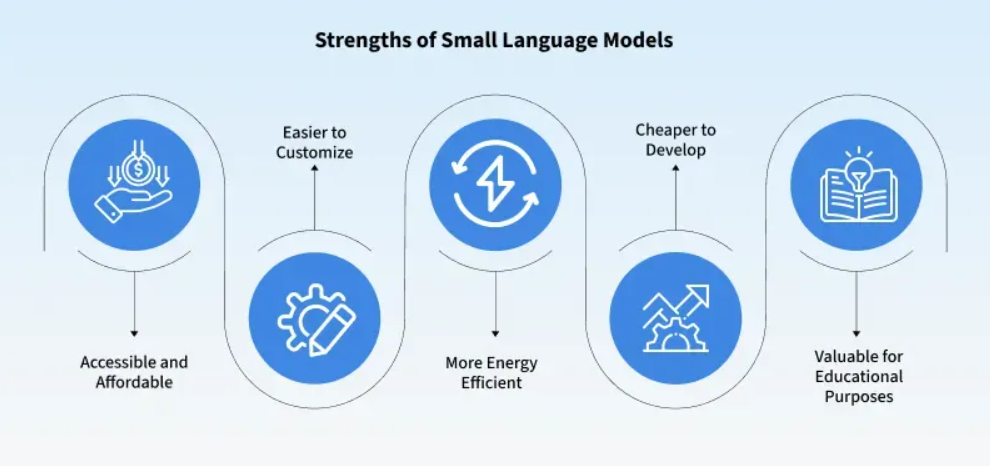
The Architecture of Efficiency
SLMs utilize the same Transformer architecture as their larger counterparts but are optimized through four key engineering strategies:
- Decoder-Only Focus: Optimized for predicting the next word, making them highly efficient for chat and text generation.
- Knowledge Distillation: A “Teacher-Student” method where a large model (Teacher) trains the SLM (Student) to match its logic, capturing “intelligence” without the “weight.”
- Quantization: Shrinking model weights from 32-bit to 4-bit or 8-bit integers. This allows a model to run on a standard smartphone or laptop CPU with almost no loss in performance.
- Grouped-Query Attention (GQA): A mathematical trick that reduces memory usage when processing long documents, drastically boosting speed.
2026 Statistics: The SLM Takeover
The data from the last 12 months confirms that frontier companies are moving away from monolithic AI.
- 3x Usage Growth: Gartner projects enterprises will use task-specific models three times more than general LLMs by 2027.
- Market Boom: The global SLM market is projected to reach $32 billion by 2034.
- Proven ROI: 75% of IT decision-makers report that SLMs outperform LLMs in speed, accuracy, and ROI for specific business tasks.
The Economics of the “Model Gap”
The core reason behind the 90% cost reduction is the massive gap in parameter counts. A “Frontier LLM” requires massive clusters of high-end NVIDIA H100 GPUs. In contrast, an SLM operates on significantly leaner architecture.
Cost and Performance Comparison
The Bottom Line: For an enterprise processing 100 million tokens a month, switching to a fine-tuned SLM is the difference between a $600,000 annual bill and a $6,000 one.
Also read How NLP Is Shaping Fintech and Healthcare Apps?
Why Small is the New Big: 4 Strategic Pillars
1. Superior Domain Expertise
LLMs are “Jacks of all trades, masters of none.” SLMs are designed for Targeted Learning. By training a 3B parameter model on a curated dataset of a company’s own data, businesses create a “Specialist” that isn’t “diluted” by the entire internet’s worth of noise.
2. Radical Latency Improvements
In user-facing applications, milliseconds matter. Heavy LLMs suffer from “inference lag.” SLMs offer sub-100ms response times, providing the “instant” feel required for voice assistants, gaming NPCs, or real-time translation.
3. Privacy and “On-Prem” Sovereignty
Because SLMs require so little compute, they can be deployed on-premise or on edge devices. This gives companies 100% control over their data, eliminating the need for expensive third-party cloud wrappers.
4. Sustainability and ESG Goals
Running massive models is an environmental nightmare. SLMs can reduce AI-related energy consumption by up to 90%, helping companies hit their carbon footprint targets.
Case Study: AT&T’s “Master-Agent” Strategy
In early 2026, AT&T moved its automated customer support to a fleet of fine-tuned Mistral and Phi models.
- The Result: A 90% reduction in monthly API costs and a 70% improvement in response speed.
- The Strategy: They use a large reasoning model as a “Master Controller” for planning, while specialized SLMs handle the actual execution of tasks.
Explore Choosing the Right Generative AI Model for Your Next Project
The Top SLMs of 2026
If you are looking to downsize your budget, these are the leaders:
- Microsoft Phi-4: The “gold standard” for reasoning at a tiny scale.
- Mistral 8B / Ministral: The most efficient models for enterprise chatbots.
- Google Gemma 3: A powerhouse for multilingual and multimodal tasks.
- Llama 4 “Scout” (Meta): The open-source favorite for private fine-tuning.
How to Start Your AI “Downsizing” Journey
- The Audit: Identify high-volume, repetitive tasks like sentiment analysis or data extraction.
- The Cascade: Implement a router. Send simple queries to the $0.30 SLM and only escalate complex reasoning to the expensive LLM.
- The Fine-Tune: Use your company’s own data to turn a generic SLM into a proprietary business asset.
Conclusion: The Era of “Right-Sized” AI
At Mindster, we specialize in bridging this gap between AI potential and production reality. Whether you are building an AI MVP or scaling a global enterprise platform, our expertise in Product Engineering and AI services ensures your architecture is lean, secure, and future-ready. In 2026, the smartest companies aren’t asking “How big can we go?” They’re asking “How small can we get?”

Professional content writer Akhila Mathai has over four years of experience. She writes posts about the different mobile app solutions we offer as well as services related to them. Her ability to conduct thorough research and think critically enables her to produce excellent, authentic, and legitimate content. Along with her strong communication abilities, she collaborates well with her teammates to create information that is current and relevant to emerging technology.