How mobility solutions in healthcare improve patient care at hospitals?
17 Oct 25 


Mobile health technology is fundamentally transforming how healthcare is delivered, monitored, and experienced. By enabling real-time access to medical data, improving care coordination, and empowering patients through digital tools integrated into smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices, mobility solutions are addressing longstanding challenges in healthcare delivery. As the industry grapples with rising patient volumes, increasing costs, and the demand for better outcomes, these technologies have emerged as essential enablers of high-quality, efficient, and patient-centered care.
Understanding Healthcare Mobility Solutions
Healthcare mobility solutions encompass mobile applications, wearable devices, and digital platforms that allow patients and providers to access, manage, and share health information anytime and anywhere. These sophisticated systems integrate seamlessly with Electronic Health Records (EHRs), hospital management systems, and telemedicine platforms to streamline workflows, reduce administrative burdens, and enhance clinical decision-making. The technology combines cloud computing, wireless communications, advanced analytics, and user-centered design to deliver comprehensive healthcare experiences that extend far beyond traditional hospital walls.
Modern mobility solutions include several critical components. Mobile clinical applications provide healthcare professionals with point-of-care access to patient information, clinical guidelines, drug databases, and diagnostic support tools. Patient engagement platforms empower individuals to actively participate in their care through symptom tracking, medication management, and secure communication with care teams. Remote monitoring systems leverage connected devices to continuously collect physiological data, enabling proactive intervention and reducing the need for frequent in-person visits. Key features include real-time data access, secure team communication, remote patient monitoring, digital appointment scheduling, and automated medication alerts.
How Mobility Solutions Improve Patient Care
Faster Access to Critical Information
Mobile-enabled EHRs allow doctors and nurses to instantly retrieve patient histories, lab results, and imaging reports during rounds or emergencies, significantly reducing diagnostic delays. A study cited in the BMJ Quality & Safety journal found that transitioning from paper to electronic records reduced death rates by 15%, highlighting the life-saving potential of digitized data access.
Enhanced Care Coordination
Mobility tools eliminate communication silos between departments such as labs, intensive care units, and outpatient clinics. Secure messaging, video consultations, and real-time updates ensure that all care providers are aligned on patient status, reducing redundant tests and errors. For example, lab results can be sent directly to a physician in surgery without physical delivery, enabling faster interventions.
Real-Time Decision Support
Mobile apps equipped with clinical calculators and AI-driven diagnostics assist physicians in making rapid, evidence-based decisions. These tools can compute risk scores, predict drug interactions, and recommend treatments based on patient-specific parameters, minimizing errors in high-pressure environments.
Remote Patient Monitoring
Wearable devices like smartwatches and glucose monitors transmit vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels in real time. This continuous data stream allows clinicians to detect early warning signs of deterioration—especially in chronic disease patients—enabling timely interventions that reduce hospital readmissions.
Improved Patient Engagement
Patients use mobile apps to track symptoms, view lab results, refill prescriptions, and communicate with providers—all from their homes. This active involvement fosters better treatment adherence and a sense of ownership over health outcomes. Personalized push notifications for medication or appointments further enhance engagement and reduce no-shows.
Streamlined Hospital Operations
Digital check-ins, automated billing, and centralized dashboards minimize paperwork and administrative delays. Nurses benefit from mobile task managers that send reminders for medication administration and shift changes, ensuring timely care delivery and reducing human error.
Expanded Access Through Telemedicine
Telehealth platforms integrated into mobile apps enable virtual consultations, especially beneficial for patients in rural or underserved areas. These remote visits support post-operative follow-ups, chronic disease management, and mental health services, reducing the need for travel and improving continuity of care.
Measurable Benefits of Mobility in Hospitals
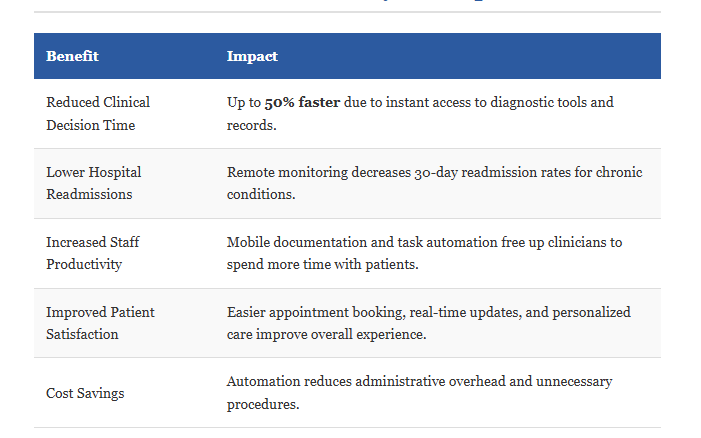
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
Despite significant benefits, mobility solutions face challenges that healthcare organizations must address. Data privacy and security risks remain paramount, especially with HIPAA compliance requirements. Mobile devices require proper encryption, multi-factor authentication, and remote wipe capabilities to protect sensitive information. Integration with legacy EHR systems can be technically complex and costly, particularly for smaller facilities lacking extensive IT resources. Interoperability standards like FHIR are improving data exchange, but implementation remains challenging. Successful adoption depends critically on user-friendly design, comprehensive staff training, and engagement of clinical champions who can advocate for the technology. Organizations must also address connectivity infrastructure, as many healthcare facilities have inadequate wireless coverage, and rural areas may lack sufficient cellular connectivity for remote monitoring.
The Future Landscape
The global healthcare mobility market is growing rapidly, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, Internet of Things devices, blockchain technology, and 5G networks. Future innovations include AI-powered diagnostic assistants that analyze medical images and predict patient deterioration, blockchain-secured patient data sharing that provides immutable audit trails and patient-controlled access, and augmented reality for surgical planning and medical training. As 5G networks expand, ultra-low latency will enable capabilities like remote surgery, while massive device connectivity will support dense IoT sensor deployments throughout hospitals and homes.
Conclusion
Healthcare leaders aiming to modernize patient care should consider partnering with experienced developers to build secure, interoperable, and scalable mobile solutions tailored to their clinical workflows. Success requires clear objectives, early clinician engagement, prioritization of integration and security, and commitment to comprehensive training and support. By embracing mobility strategically, hospitals can deliver safer, more efficient, and patient-centered care in an increasingly digital world. The transformation is not merely technological but represents a fundamental reimagining of healthcare delivery that puts information, tools, and empowerment directly into the hands of patients and providers, ultimately improving outcomes and experiences across the entire care continuum.
- Agentic AI1
- Android Development3
- Artificial Intelligence38
- Autopay1
- Classified App3
- Custom App Development5
- Digital Transformation12
- Doctor Appointment Booking App14
- Dropshipping1
- Ecommerce Apps40
- Education Apps2
- Fintech-Apps38
- Fitness App4
- Flutter4
- Flutter Apps20
- Food Delivery App5
- Grocery App Development1
- Grocery Apps3
- Health Care10
- IoT2
- Loyalty Programs11
- Matrimony Apps1
- Microsoft1
- Mobile App Maintenance2
- Mobile Apps132
- On Demand Marketplace1
- Product Engineering6
- Progressive Web Apps1
- React Native Apps2
- Saas Application2
- Shopify9
- Software Development3
- Taxi Booking Apps7
- Truck Booking App5
- UI UX Design8
- Uncategorized7
- Web App Development1



















Comments