Why Neobanks are the Future of Banking: A Comprehensive Guide
18 Mar 24 


“Neobanks are changing the way we bank, making it easier and more user-friendly. They are expected to make $300 billion by 2025, mostly from fees, loan interest, and subscription services. This makes them a major player in the financial world”.
In a world where we’re accustomed to lightning-fast 5G internet and 15-minute food delivery, the idea of waiting a whole day for a transaction to process can be incredibly frustrating. People want banking to be fast, easy, and end users. While big banks and tech-savvy finance companies are trying to catch up with what end users want, there’s a new player in town shaking things up – neobanks.
Neobanks are like money bridges, connecting businesses with customers through secure digital money services. Also, they stand out from traditional banks in their last-mile reach. With digitally-enabled capabilities, now people in remote areas can avail banking services and offerings, ensuring better financial inclusivity.
However, before we discuss whether neobanks are better than traditional banks, let’s make sure we understand what neobanks are.
What is neobank?
Neobanks are a type of online financial institution that provides essential banking services using advanced technology. Unlike traditional banks, neobanks operate exclusively online through mobile apps or web platforms, without physical branch locations. Customers can easily open accounts, manage their finances in real time, and make online transactions from anywhere.
Neobank VS traditional banks
Neobanks and traditional banks have some key differences that set them apart in terms of their services and target audience. Neobanks, also known as online banks, are entirely digital banks that offer banking services through mobile apps and websites. They typically have lower fees and offer more innovative features, such as budgeting tools and personalized savings goals, compared to traditional banks.
On the other hand, traditional banks have a physical presence with brick-and-mortar branches and offer a wide range of services, such as mortgages, loans, and investment management. They also provide more face-to-face customer support and have a longer-established reputation in the banking industry. Ultimately, the choice between a neobank and a traditional bank comes down to personal preference and financial needs.
Having realized the potential of digital offerings and the evolving customer expectations, several traditional banks are quickly adopting digitization.
Additionally, neobanks may partner with traditional banks to leverage their established infrastructure and regulatory compliance. This allows neobanks to offer a wider range of services to their customers and provides a level of trust and stability that many customers seek when considering a new financial institution.
What makes neobank and digital banks divergent?
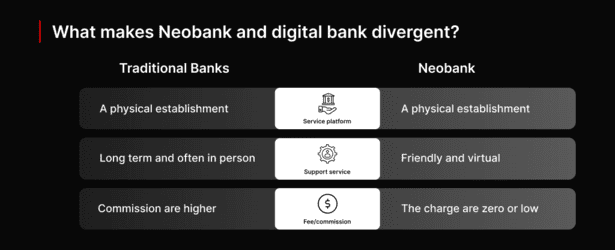
Neobanks and digital banks may share similarities, but they are distinct types of financial institutions with unique operational models and offerings. Neobanks and digital banks are often used interchangeably, but they are distinct.
A digital bank is a traditional bank that has moved its services online, allowing customers to access their accounts and complete transactions through a digital platform. On the other hand, a Neobank is a completely digital bank that operates without a physical branch.
Neobanks often offer a more streamlined and user-friendly experience than traditional banks, with features such as budgeting tools and real-time spending alerts. Additionally, The primary revenue sources of neo banks are various transaction and service fees, and interest on loans and deposits.
How does neobank make revenue?
Neobanks, primarily make money through various fees and interest on loans and deposits. According to a report by Accenture, neobanks globally are expected to generate around $300 billion in revenues by 2025. Interchange fees, charges paid by merchants to banks when customers use debit/credit cards to complete a transaction also constitute a stream of revenue.
“According to a report by The Economist, in the UK, neobanks make around 20% of their revenue from interchange fees”.
Neobanks also generate revenue by charging fees for various services such as overdrafts, ATM withdrawals, foreign currency transactions, and others. For example, Revolut, a UK-based neobank, charges a monthly subscription fee for its premium service, which offers additional features such as travel insurance and cashback on purchases.
Another way neobanks make money is by offering loans and collecting interest on them. According to a report by McKinsey, neobanks in Europe have been able to generate a return on equity of around 10% through their lending activities.
Overall, neobanks have been able to disrupt the traditional banking industry by offering cheaper and more convenient banking services. As per the forecasts, their revenue is expected to grow significantly over the next few years, making them a force to be reckoned with in the financial services industry.
Now that we have a good understanding of neobanks, let’s explore the advantages and disadvantages of these Neobanks.
Revenue sources of neobanks
Neobanks generate revenue through various sources, which contribute to their overall profitability and growth. The primary revenue sources of neobanks include:
- Interchange fees: Neobanks earn a significant portion of their revenue through interchange fees. When customers use a card issued by the neobank to make a payment, the neobank collects an interchange fee. For example, Varo generates 98% of its revenue from interchange fees, and Chime is a well-known example of a neobank that pursues this business strategy.
- Interest on loans and credit cards: Neobanks charge interest on loans and credit cards, which also contributes to their overall revenue. This includes profit from balances carried and their associated interest rates.
- Transaction fees: While most neobanks don’t charge fees for accounts, they may charge small fees for bank transfers, ATM withdrawals, or money transfers.
- Subscription fees: Some neobanks offer premium services in exchange for a monthly subscription fee.
These revenue sources, in addition to other strategies, contribute to the financial success of neobanks and enable them to compete effectively in the financial industry.
Advantages of neobanks
- Convenience: Neobanks provide a seamless and convenient digital banking experience, often with intuitive mobile apps and user-friendly interfaces that allow customers to manage their finances anytime, anywhere.
- Lower fees: Many neobanks have lower fees compared to traditional banks, offering reduced or zero fees for services such as international transactions, currency exchange, and ATM withdrawals.
- Innovative features: Neobanks are known for their innovative features and technologies, such as AI-driven financial insights, automated saving tools, real-time transaction notifications, and personalized budgeting assistance.
- Accessibility: Neobanks are accessible 24/7 from anywhere with an internet connection, providing convenience for customers who prefer digital banking over traditional branch-based banking.
- Specialized services: Some neobanks focus on niche services, catering to specific customer needs such as travel-friendly accounts, cryptocurrency support, or socially responsible investing options.
Disadvantages of neobanks
- Limited product offerings: Neobanks may have a more limited range of financial products compared to traditional banks, potentially lacking certain services like mortgage lending, extensive investment options, or specialized business banking solutions.
- Security concerns: As with any digital platform, there are inherent cybersecurity risks associated with neobanks, although they are regulated and adhere to security standards to protect customer data and transactions.
- Customer support: Some customers may find neobanks offer less personalized customer support compared to traditional banks, as they rely heavily on digital communication channels and may not have physical branches for in-person assistance.
- Dependence on technology: Neobanks are reliant on technology, and any technical outages or disruptions could impact a customer’s ability to access their funds or manage their accounts, highlighting the importance of robust IT infrastructure and contingency plans.
- Trust and familiarity: Some consumers may still have reservations about trusting their finances to a relatively new and unfamiliar type of financial institution, preferring the established reputation and physical presence of traditional banks for a sense of security and familiarity.
Bottom line
Neobanking emerged to address the significant digital transformations in the financial sector, and it has successfully met these expectations. Customers now enjoy the benefits of neobank features, avoiding the traditional banking process and conducting their financial transactions according to their preferences.
Looking for a reliable solution to develop your neobank? Look no further than Mindster, a leading app development company that specializes in fintech services. With their expertise in creating innovative and secure financial technology solutions, Mindster is the perfect choice for building and customizing your neobank to align with your specific requirements. Contact Mindster today to explore how their fintech services can empower you to launch your neobank successfully.
- Agentic AI1
- Android Development3
- Artificial Intelligence36
- Classified App3
- Custom App Development5
- Digital Transformation12
- Doctor Appointment Booking App14
- Dropshipping1
- Ecommerce Apps40
- Education Apps2
- Fintech-Apps38
- Fitness App4
- Flutter4
- Flutter Apps20
- Food Delivery App5
- Grocery App Development1
- Grocery Apps3
- Health Care10
- IoT2
- Loyalty Programs9
- Matrimony Apps1
- Microsoft1
- Mobile App Maintenance2
- Mobile Apps130
- Product Engineering6
- Progressive Web Apps1
- React Native Apps2
- Saas Application2
- Shopify9
- Software Development3
- Taxi Booking Apps7
- Truck Booking App5
- UI UX Design8
- Uncategorized6
- Web App Development1



















Comments